Premium CTP Plates • Photopolymer Films • Printing Inks • Accessories
Table of Contents

1. Introduction: The Role of CTP Plates in Modern Printing
Offset printing remains the dominant method for high-volume, high-precision commercial printing. Brochures, magazines, packaging, books, labels, and marketing materials all rely on plates—specifically CTP plates.What is a CTP Plate?
A CTP plate is a specially coated aluminum plate that receives images directly from a laser imaging device, eliminating traditional film-based workflows. The laser alters the coating’s structure, forming hydrophobic (ink-friendly) and hydrophilic (water-friendly) areas necessary for lithographic printing.Why CTP Matters
- Higher accuracy
- Faster plate production
- Lower material waste
- Better print consistency
- Fully digital workflow integration
2. How Does a CTP Plate Work? — The Science Behind the Process
The operation of a CTP system integrates hardware, chemistry, and precision imaging physics. Below is a full breakdown.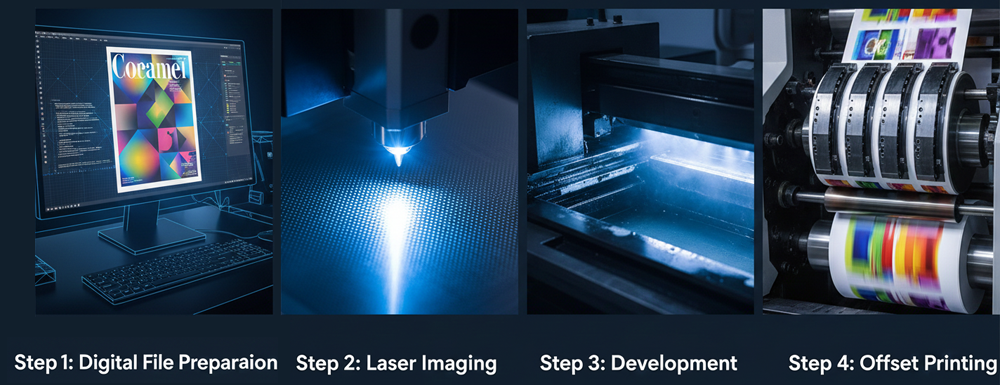
Step 1: Digital File Preparation (RIP Processing)
The workflow begins with a digital file.
A Raster Image Processor (RIP) converts vector artwork into high-resolution rasterized data, specifying:
- dot shape
- halftone patterns
- screening angles
- resolution (typically 2,400 dpi or higher)
This raster data is sent directly to the CTP engine.
Step 2: Laser Imaging on the Plate
Inside the CTP machine:
- A laser diode (thermal or violet) scans across the plate surface.
- The plate coating reacts to the laser’s energy.
- The laser engraves or changes the solubility of the coating.
The imaging mechanism depends on plate type:
| Plate Type | Reaction | Light Source |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Plate | Heat changes polymer structure | 830 nm IR laser |
| Violet Plate | Photochemical reaction | 405 nm violet laser |
| Process-Free Plate | Thermal micro-structural change | 830 nm laser |
| UV-CTP Plate | Photoreaction | UV laser |
The output is a precise reproduction of the digital design on an aluminum substrate.
Step 3: Development or On-Press Processing
After imaging, plates undergo either:
A. Standard Development
Plates are processed in a developer unit:
- exposed areas dissolve
- unexposed areas remain
This forms the ink-receptive image.
B. Process-Free or Chemistry-Free Plate Processing
Plates go directly onto the press:
- the press’s dampening and inking systems remove non-image areas
- the image area strengthens during the first few hundred impressions
This reduces chemicals, waste, and environmental impact.
Step 4: Mounting the Plate on the Offset Press
Once ready, plates are clamped onto the press cylinder.
The printing process begins:
- Non-image areas attract water.
- Image areas attract ink.
- Ink transfers to the blanket cylinder.
- The blanket prints onto paper.
This indirect printing method provides the extremely crisp detail offset is known for.
3. Types of CTP Plates: Materials, Coatings, and Performance Differences
Different applications require different plate characteristics. Here are the major categories:

3.1. Thermal CTP Plates
Most widely used due to stability and precision.
Features:
High resolution (1–99% dots at 200–400 lpi)
Excellent plate durability
Resistance to ambient light
Typically supports long print runs
Ideal For:
High-end commercial printing, packaging, magazines, books.
3.2. Violet CTP Plates
Uses 405 nm violet laser imaging.
Advantages:
Lower equipment cost
Fast imaging speed
Energy-efficient
Limitations:
Requires safelight or protection from UV
Shorter shelf life
Best For:
Newspaper printing, mid-volume jobs.
3.3. UV-CTP Plates
Designed for UV laser exposure.
Advantages:
Low-cost plates
Compatible with existing UV workflow
Suitable for regions with tight budgets
Use Cases:
Small to medium commercial printers.
3.4. Process-Free / Chemistry-Free Plates
Environmentally friendly modern solution.
Benefits:
Zero developer chemicals
Zero waste liquid
Immediate press-mounting
Lower ecological impact
Drawbacks:
Slightly lower run length compared to premium thermal plates.
Ideal Users:
Eco-focused facilities and small to mid production environments.
4. CTP Plate Structure: What’s Inside a Plate?
CTP plates are engineered for durability and precise imaging. A typical thermal plate has:
Electro-grained aluminum substrate
Provides mechanical strength and water affinity.Anodized oxide layer
Improves wear resistance.Hydrophilic interlayer
Ensures water retention for non-image areas.Photosensitive coating
Polymer or photopolymer layer that reacts to laser exposure.Top protective layer (depending on type)
Protects against oxidation and mechanical damage.
5. Key Performance Metrics of CTP Plates
When selecting a plate, printers evaluate several technical parameters:
5.1. Resolution & Dot Reproduction
High-end plates support:
200–300 lpi AM screening
20–30 µm FM stochastic screening
1–99% dot reproduction accuracy
5.2. Sensitivity & Imaging Energy
For thermal plates:
120–150 mJ/cm² is typical.
Lower energy = faster imaging.
5.3. Durability (Run Length)
Run length varies by plate type:
| Plate Type | Unbaked | Baked |
|---|---|---|
| Standard Thermal | 80k–120k | 150k–200k |
| High-grade Thermal | 150k–250k | 300k–1 million |
| Process-Free | 30k–80k | Not bakeable |
| UV Plate | 30k–100k | Optional |
5.4. Plate Bakeability
Thermal plates can be baked to extend service life, making them ideal for long magazines, packaging jobs, or catalogs.
5.5. Chemical Resistance
High-performance plates resist:
UV inks
Alcohol dampening systems
High-pressure rollers
Abrasive paper types
6. Advantages of CTP Plate Technology
6.1. Superior Print Quality
Sharper dots, smoother gradients, better color consistency.
6.2. Faster Production
No film, no contact frames—plates go from computer to press in minutes.
6.3. Reduced Waste
Eliminates film, chemicals, darkroom errors, and registration problems.
6.4. Workflow Automation
Integration with:
CIP3/CIP4
Prepress workflows
Imposition software
Color management systems
6.5. Environmental Benefits
fewer chemicals
less water consumption
reduced energy usage
6.6. Lower Operating Costs
Less manual intervention and fewer consumables.
7. Common Applications of CTP Plates
CTP plates are used in virtually all offset print sectors, including:
Commercial printing (magazines, brochures, flyers)
Packaging printing (cartons, labels, foils)
Book manufacturing
Newspaper printing
Security and specialty prints
Process-free plates are increasingly popular in corporate in-house print rooms or small shops.

8. Future Trends in CTP Plate Technology
The printing industry continues to evolve. Emerging trends include:
1. Fully Process-Free Workflows
Reducing chemical use is becoming the global standard.
2. High-Durability Low-Energy Plates
Lower laser energy = faster throughput.
3. Hybrid Offset–Digital Integration
CTP systems now feed data to both offset and digital workflows.
4. Sustainable Manufacturing
Recyclable plates and low-carbon production processes will become mainstream.
5. AI-Enhanced Prepress Automation
Automatic dot correction, exposure optimization, and predictive maintenance.
Conclusion
CTP plates form the foundation of the modern offset printing workflow. Their precise imaging, durable aluminum structure, and chemical engineering allow high-volume production with superb print quality. Whether choosing thermal, violet, UV, or process-free plates, understanding how they work empowers print professionals to optimize output, reduce waste, and achieve consistent results.
As the printing industry moves toward greener and more automated future technologies, CTP plates will remain essential tools connecting digital design to physical print.

What Is the Cost of CTP Plate? Complete Pricing Guide for Thermal, Violet & Process-Free CTP Plates
Guide explaining the true cost of CTP plates, including price ranges, cost per m², thermal vs. violet vs. process-free plate cost, run-length comparison, and practical tips to reduce printing expenses. Accurate, SEO-optimized, and easy to understand.

What Is a CTP Plate and How It Works | Comprehensive Guide to Modern Offset Printing Plates
Learn what a CTP plate is, how the computer-to-plate process works, and the differences between thermal, violet, UV, and process-free plates.

Violet Laser Offset Plate
The Violet Laser Offset Plate is a high-performance photopolymer CTP plate engineered for violet laser (405 nm) imaging systems.
Message
Contact us
Locate and visit us or send us a message for next project!